The Male Reproductive System

The Scrotum: supporting structure for the two testes; looks like single pouch of skin separated into lateral portions by median ridge called raphe.
Scrotal septum: the internal septum of the scrotum keeps each testis in its own sac.
Testes: paired oval shaped glands in the scrotum out side the body cavity to have lower temperature for the spermatogenesis.
Tunica vaginalis: serous membrane derived from the peritoneum surrounding the testis.
Tunica albugenea: deeper membrane surrounding the testes.
Lobules: each testis is divided by the tunica albugenea into many lobules.
Seminiferous tubule: tightly coiled tubule contained in the lobule.
Spermatogenic cells : sperm-forming cells.
Sertoli cells: supporting cells for the spermatogenic cells acting as blood-testes-barrier.
Leydig cells: testosterone-secreting cells.
Epididymis: highly convoluted tubule, 4cm long,lies along the posterior side of each testis; functions in the sperm maturation and storage.
Ductus deferens=Vas deferens: 45 cm long ascends along the posterior border of epididymis passes through inguinal canal and enters the pelvic cavity, looping over ureter and curves to posterior side of the urinary bladder.
Spermatic cord: supporting structure ascends out of the scrotum, consists of vas deferens, testicular blood and lymphatic vessels,nerves and cremaster muscle.
Ejaculatory duct: 2cm long formed by union of duct from the seminal vesicle and ampulla of vas deferens and terminates in prostatic urethra.
Urethra: shared duct between the urinary and reproductive systems. Prostatic, membranous and spongy are the divisions of the male urethra, opens at the external urethral orifice.
Accessory glands:
Seminal vesicle: paired convoluted pouch-like structures, lying posterior to the urinary bladder and anterior to the rectum. The secretion is mainly alkaline viscous fluid contains the fructose as source of energy for the sperm.
Prostate gland: single, doughnut-shaped gland, inferior to the urinary bladder and surrounds the prostatic urethra. Secrets milky acidic fluid.
Bulbourethral glands=Cowper's glands: bea-sized gland, located inferior to the prostatic gland on either sides of membranous urethra. Secretion of these glands is alkaline fluid to neutralize the urethra from urine.
Penis: consists of three parts; body, glans penis and root. It contains the spongy urethra to exit the urine as well as the semen out of the body.
The Female Reproductive System
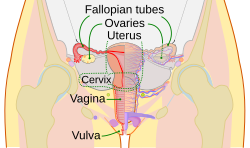
The ovaries : two almond size and shaped glands for the ova synthesis. Each one is surrounded by tunica albugenea. Each one contains cortex which contains the follicles and medulla which contains the blood and lymphatic vessels and nerves.
Mesovarium: double-layered fold of the peritoneum attach the ovaries with the broad ligament of the uterus.
Ovarian ligament: anchors the ovaries to uterus.
Suspensory ligament: attaches the ovaries to the pelvic wall.
The uterine tubes=the oviducts:
· Infundibulum: funnel shaped structure facing the ovary very closely and opens at the pelvic cavity.
· Fimbriae: finger like projections at the end of each infundibulum toward each ovary.
· Ampulla: the upper widest longest portion of the tube.
· Isthmus: the medial short narrow thickened wall of the tube.
The uterus:
· Fundus: most superior dome-shaped portion.
· Body: tapering central portion.
· Cervix: inferior narrow portion, opens into the vagina.
· Uterine cavity: internal cavity of the uterus.
Cervical canal: internal cavity of the cervix.
Broad ligament: double folds of the peritoneum attach the uterus to the pelvic wall.
Uterosacral ligament: peritoneal extensions, attach the uterus to the sacrum.
Cardinal ligaments: at the base of the broad ligament, extend from the pelvic wall to the cervix and vagina.
Round ligaments: bands of fibrous connective tissue between the layers of the broad ligament.
The vagina
10 cm long tube, extends from the cervix inferiorly to the exterior of the body as the vaginal orifice.








0 comments:
Post a Comment