OBJECTIVES:
· To identify the vertebra as a special type of bone
· To distinguish between vertebrae from the different regions of the vertebral column
· To identify the rib and its own structures and the structures of the sternum
· To be familiar with the different types of ribs
1** The Vertebral Column
The vertebral column is built up from 26 bones in adult person, each one is called vertebra. The vertebral is found for spinal cord protection and muscle attachment site. The vertebrae are divided into five regions:
1. the cervical region
2. the thoracic region
3. the lumbar region
4. the sacral region
5. the coccygeal region
The general structure of the vertebra is reserved in the different region with having special features for each region of the vertebral column. Each vertebra has a projection at its posterior side called spinous process , also it has a large foramen at its center called vertebral foramen, the successive foramina build up the vertebral canal for the spinal cord passage. The body of the vertebra which contains the bulk of the bony tissue is located anteriorly, the body of the successive vertebrae are separated by the presence of intervertebral disks to protect them against friction. At the two lateral side, each vertebra holds projections called transverse processes mainly for muscle attachment. The two superior articular facets exist at the superior surface of the vertebra to articulate with the above one laterally, while the two inferior articular facets are located at the inferior surface of the same vertebra for articulation with the lower one laterally. Lamina is the bony mass that connects between the spinous process and the transverse process, while the pedicle is that mass lies between the transverse process and the body of the vertebra. The vertebrae of different regions have specific differences in their structure which will be discussed as following:
1. The cervical vertebrae
* 7 vertebrae are found.
* the first one= atlas lost its body and spinous process.
* the second one= axis gained excess body directed superiorly called dens.
* each one of the cervical vertebrae contains two transverse foramina laterally.
* the spinous processes for vertebrae C2-C6 are bifid.
* the spinous process of the seventh one is prominent.
2. The thoracic vertebrae
* 12 vertebrae are found.
* the spinous process of each one is directed slightly to the inferior side.
* each vertebra holds pair of superior articulation demifacets and pair of inferior articulation demifacets at the base of the body for articulation with rib laterally.
* the heart-shaped body of thoracic vertebra is smaller than that of the lumbar vertebra.
3. The lumbar vertebrae
* 5 vertebrae are found.
* the large and bulky body is will characterized and takes the shape of kidney.
4. The sacral vertebrae
* one sacrum is found but composed of 5 fused sacral vertebrae.
* inverted triangular-shaped bone; the wide base is directed superiorly and narrow apex is directed inferiorly.
* the bodies of the successive vertebrae are fused as well as the transverse processes.
* no intervertebral disks are found, instead there are 4 trasverse lines.
* 4 pairs of anterior sacral foramina and posterior sacral foramina are found.
* anteriorly, the sacral canal, sacral hiatus and median sacral crest are found.
* the sacral cornu is found as pair located laterally at the most inferior point of sacrum.
* at the two lateral sides of sacrum, the sacral tuberosities are found.
5. The coccygeal vertebrae
* one coccyx is found composed of 4 fused vertebrae.
* the coccygeal cornu found as pair at the superior side of the bone.
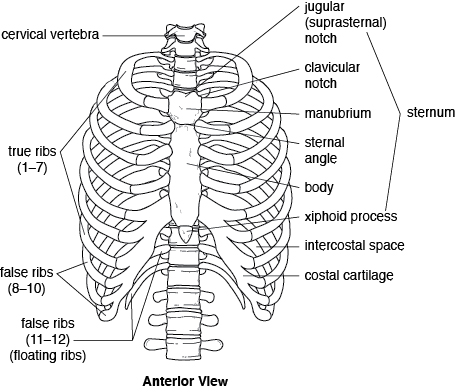
2** The thoracic cage
The thoracic cage is composed of 12 pairs of ribs and a single bone called sternum. Each rib is composed of head, neck and shaft. The rib articulates with the thoracic vertebra by two points; the head of the rib with the articular semifacet and the articular part of the tubercle with the transverse process of the thoracic vertebra. The rib articulates with the thoracic vertebra medially at the posterior side then directs laterally and bens at the angle anteriorly and medially until it reaches the sternum anteromedially. According to the articulation with the sternum, the ribs are classified into three types: 1. true ribs= each rib articulates with the sternum individually by its own costal cartilage, the ribs from 1-7 are considered as true ribs.
2. false ribs= group of ribs sharing the same costal cartilage, the ribs 8,9 and 10 are false ribs.
3. floating ribs= the ribs that don't articulate with the sternum at all, the 11th and 12th ribs are floating ribs.
The sternum is a flat bone located at the middle anterior side of the chest, it is composed of three structures: ** the manubrium which is the most superior part, has a depressed surface located superiorly called the suprasternal notch. This structure articulates with the clavicle and the first and second ribs.
** the body which the longitudinal part direct inferiorly, articulates with the 3rd till 10th ribs.
** the xiphoid process is the most inferior part of the sternum composed of cartilaginous tissue will be ossified after age of 40. it doesn't articulate with ribs.








0 comments:
Post a Comment